Central bank play an important role in managing a country’s monetary policy, regulating the money supply, and ensuring financial stability. Therefore, understanding how central banks work is essential for investors, businesses, and policymakers. Follow the content below to better understand these roles!
What is a Central Bank?
A central bank is an essential financial institution of a country, responsible for managing and overseeing the monetary and financial system. Its main duties include issuing currency, adjusting interest rates, and controlling the money supply to ensure economic stability and manage inflation.

Additionally, the central bank supervises the activities of commercial banks to ensure a safe and sound banking system. When necessary, it acts as a “lender of last resort” to assist commercial banks facing financial difficulties. The central bank also manages foreign currency reserves and intervenes in the foreign exchange market to stabilize the national currency’s value.
See more:
- The most effective way to master a live account in stocks
- What is a Demo Account? How to Choose an Account in Forex
- Instructions how to use the Economic Calendar updated daily
- What is Financial News in Forex? How to Read New Effectively
The Biggest Central Banks
The biggest Central Bank, known for their significant influence on the global financial system, include:
- Federal Reserve (Fed): The central bank of the United States, which plays a crucial role in global finance due to the size and importance of the U.S. economy. It sets monetary policy, regulates banks, and provides financial services to the government.
- European Central Bank (ECB): Responsible for monetary policy within the Eurozone, which consists of 19 European Union member countries that use the euro. The ECB aims to maintain price stability and support economic growth within the Eurozone.
- People’s Bank of China (PBOC): The central bank of China, which manages the country’s monetary policy and foreign exchange reserves. Its policies have a major impact on global markets due to China’s large and growing economy.
- Bank of England (BoE): The central bank of the United Kingdom, which is responsible for monetary policy, financial stability, and regulating financial institutions in the UK.
Central Banks with Low Interest Rates
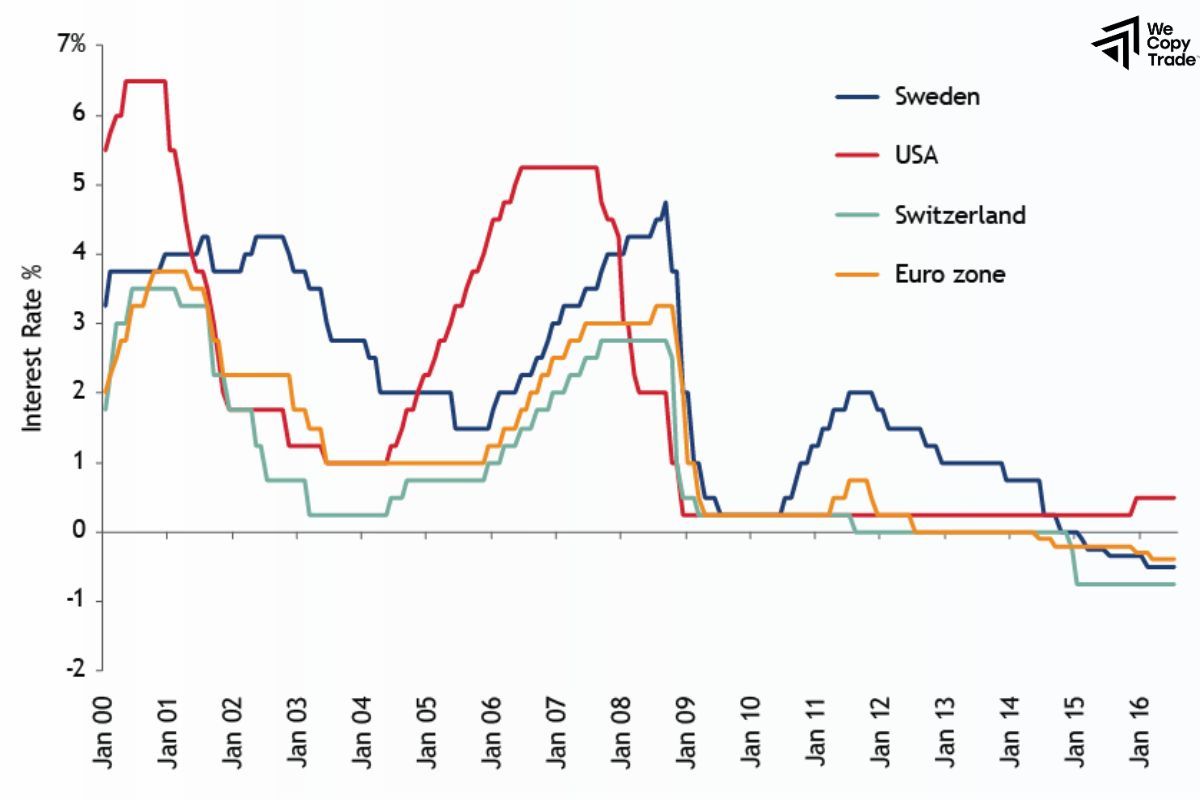
Central Bank with low interest rates are often aiming to stimulate economic growth and combat low inflation or economic stagnation. Here are some central banks known for maintaining low interest rates in recent years:
- European Central Bank (ECB): The ECB has kept interest rates low to support economic growth and combat low inflation across the Eurozone. The policy includes negative interest rates on deposits to encourage borrowing and investment.
- Bank of Japan (BoJ): The BoJ has maintained a policy of low or negative interest rates for years to stimulate economic activity and combat deflation in Japan. It also engages in extensive asset purchases to inject liquidity into the economy.
- People’s Bank of China (PBOC): While not as aggressive as the ECB or BoJ, the PBOC has used low interest rates and other monetary easing measures to support economic growth and manage economic challenges.
- Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA): The RBA has maintained low interest rates to stimulate economic growth and support employment, especially during periods of economic slowdown.
- Bank of Canada (BoC): The BoC has kept interest rates low to support economic recovery, particularly in response to economic disruptions and challenges.
The Role of Central Banks in the Economy 2024
In 2024, the Central Bank will continue to play a critical role in managing and influencing economic conditions globally. Their primary functions include:
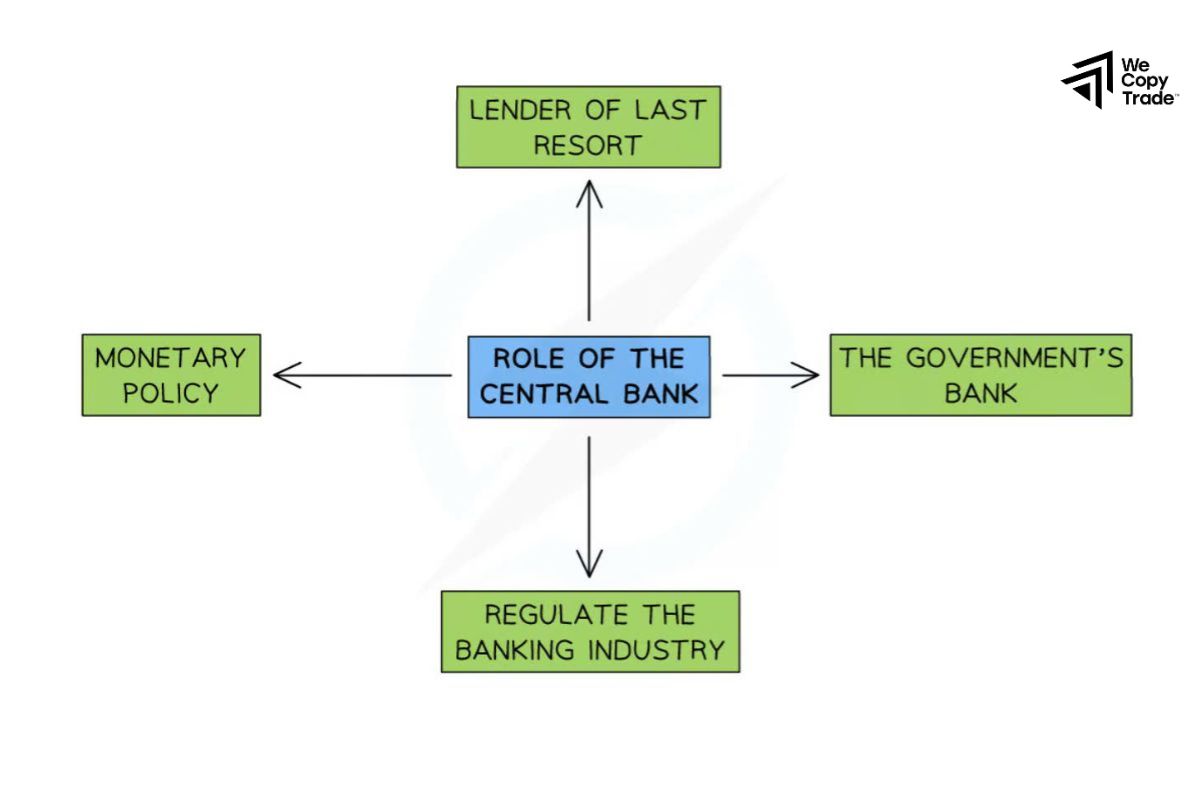
Monetary Policy
The Central Bank set interest rates and controls the money supply to manage inflation, stabilize the currency, and promote economic growth. In 2024, this involves balancing responses to post-pandemic recovery, inflationary pressures, and global economic uncertainties.
Financial Stability
They ensure the stability of the financial system by monitoring and regulating banks and other financial institutions. Central Bank act as a lender of last resort during financial crises, providing liquidity to prevent bank failures and systemic risks.
Economic Growth
By adjusting interest rates and implementing quantitative easing or tightening measures, central bank aim to stimulate economic growth or cool down an overheating economy. This involves fine-tuning policies to address varying economic conditions and challenges.
Currency Management
Central bank manage and stabilize their country’s currency by intervening in foreign exchange markets if necessary. They also manage foreign exchange reserves to support currency stability and international trade.
Support for Economic Transition
In 2024, central bank are also focusing on supporting transitions in the economy, such as digital transformation and sustainability initiatives, by adapting monetary policies and regulatory frameworks.
How Do Interest Rates Work?

Interest rates are the cost of borrowing money or the return on savings, and they play an important role in the economy. Here’s a simple breakdown of how they work:
- When you borrow money, whether it’s a mortgage, car loan, or credit card, the interest rate is the cost you pay for using a lender’s money.
- For savers and investors, interest rates determine how much return they can earn on their deposits or investments.
- Central banks that set benchmark interest rates, such as those in the United States, also influence the overall level of interest rates in the economy. They use these rates to manage economic growth and inflation.
- Typically, interest rates are adjusted based on inflation. For example, if you have a savings account that pays 5% interest but inflation is 3%, your real interest rate is 2%.
- Additionally, the central bank can adjust interest rates to control inflation and ensure that real interest rates are consistent with economic conditions.
- Market interest rates are influenced by the central bank rate but can change based on the supply and demand for credit, economic conditions, and other factors.
- For example, mortgage rates, auto loan rates, and credit card rates all fluctuate based on market conditions and central bank policy.
Do Interest Rates Affect Markets?

Yes, interest rates have a big impact on financial markets. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper, which can boost stock prices and make bonds less attractive. This often leads investors to buy more stocks. Lower interest rates also reduce the cost of mortgages, making it easier for people to buy homes and potentially increasing property prices.
By contrast, when interest rates are high, the cost of borrowing increases, which can lead to lower stock and property prices and make bonds more attractive relative to stocks. Interest rates also affect the value of currencies, as higher interest rates can attract foreign investors and strengthen the currency.
A Few Interest Rate Examples
Here are a few examples of how interest rates can affect different financial scenarios:
Savings Accounts
If your savings account offers an interest rate of 1% per year, you will earn $10 in interest for every $1,000 you deposit. A higher interest rate, say 3%, would earn you $30 on the same $1,000.
Mortgages

A 30-year fixed mortgage with a 4% interest rate means you’ll pay less in total interest over the life of the loan compared to a 5% interest rate. For a $200,000 mortgage, a 4% rate could cost you around $143,000 in interest over 30 years, while a 5% rate might cost you around $193,000.
Credit Cards
If your credit card has an annual percentage rate (APR) of 18%, and you carry a $1,000 balance, you would pay $180 in interest over a year if you don’t make any payments. A lower APR of 12% would reduce your interest payment to $120.
Bonds
Suppose you invest in a bond with a 3% interest rate. If interest rates rise to 4%, new bonds will offer better returns, making your bond with a 3% rate less attractive and potentially decreasing its market value.
Conclusion
In conclusion, central bank are crucial in steering the economy through their strategic interventions. Therefore, staying informed about central banks activities can provide key insights into economic trends and help you make better financial decisions. Keep an eye on how these powerful institutions shape the financial landscape to stay ahead in a dynamic economic environment.
See more: