Have you ever heard of doubling your investment? That’s the power of financial leverage. However, leverage also carries significant risks. This article will help you explore the world of financial leverage, from the basics to how to apply it most effectively.
What is Financial Leverage?

Financial leverage is the practice of using borrowed funds to magnify investment returns. They employ various financial instruments, such as options, futures, and margin accounts, to amplify their investments.This strategy is often employed by businesses seeking to expand, acquire other companies. In other words, instead of issuing shares to raise capital, companies can use debt financing to invest in their own businesses to impact growth.
See now:
- What is Forex? Secrets to Successful Trading for beginners
- What is a Currency Pair? A Detailed Guide to Currencies in Forex Trading
- What is Forex Spread? What are the Impacts and Types of Forex Spread?
What are leverage ratios?
Leverage ratios indicate the level of risk in your trading. The higher the leverage, the greater the risk but also the higher the potential profit. Leverage is not fixed but varies depending on the type of market. Highly volatile markets often have lower leverage to limit the risk for investors
How does financial leverage work?

When a company wants to buy a new asset, they have three main paths:
- Use their own money: That is, use equity.
- Borrow money: That is, use debt.
- Lease assets: That is, use a form of financial leasing.
Using debt allows the company to quickly own the asset immediately without having to wait too long to accumulate enough capital.
How to calculate the Financial Leverage?
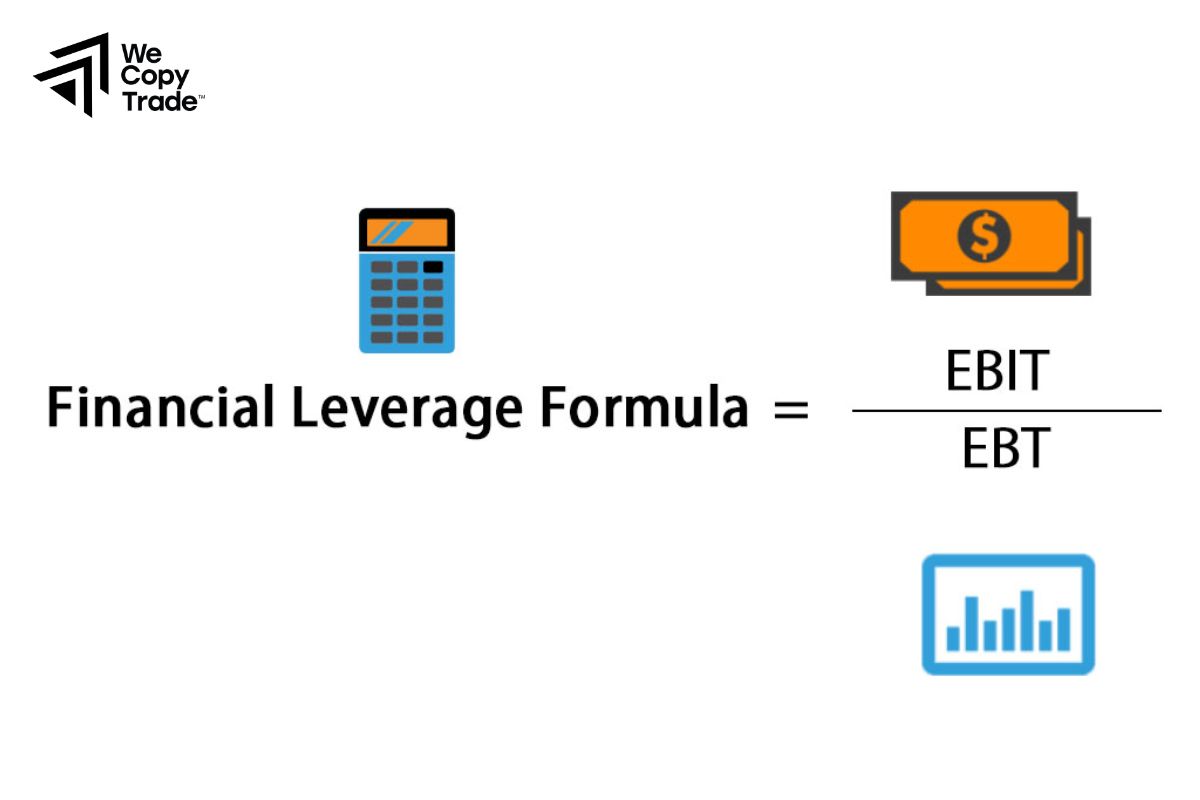
To assess the extent of financial leverage, investors and analysts often use leverage ratios. Two of the most common ratios are:
- Debt-to-equity ratio: This ratio shows how much debt a company uses compared to its equity. A high ratio indicates that the company relies heavily on debt to operate.
Debt to Equity Ratio (D/E) = Total Debt ÷ Total Equity
- Debt-to-total-assets ratio: This ratio shows the portion of debt holders’ equity in the total assets of the company. The higher the ratio, the greater the financial risk of the company.
Debt Ratio = Total Debt ÷ Total Assets
What is the relationship between Margin and Leverage?
- Margin and leverage are two inseparable concepts in trading.
- Margin is an amount of money that an investor must deposit to secure a trade, while leverage is the ability to use a small amount of money to control a larger investment. The relationship between margin and leverage is shown by the formula:
- Leverage = 1 / Margin requirement.
- The lower the margin requirement, the higher the leverage and vice versa. Margin requirements are often expressed as a percentage of the value of the trading position and are called spreads.
Which Leverage is Best for Beginners?
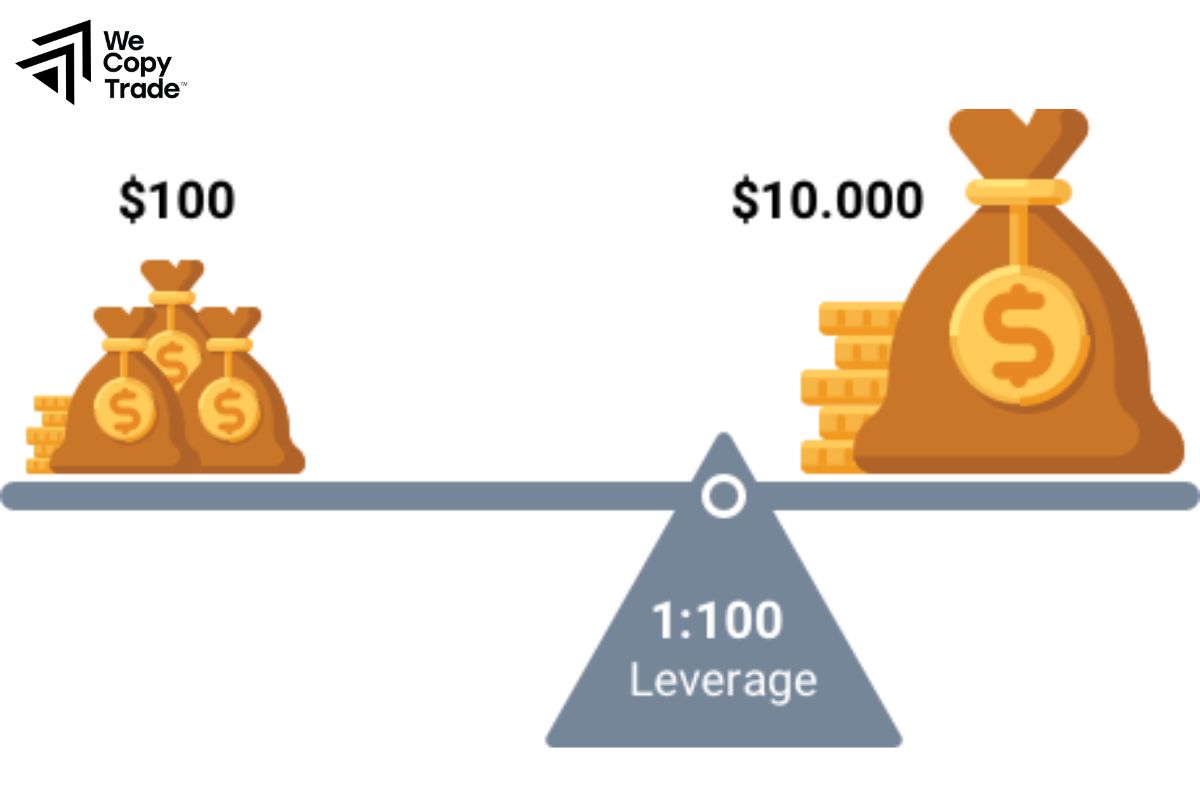
Don’t let the quick profit figures from high leverage fool you. For beginners, low leverage is the wise choice. Starting with low leverage allows you to better control your risk, learn from your mistakes and increase your confidence in the market. For example, instead of using 1:100 leverage, you should start with 1:10 or even lower leverage. This will give you enough time to get used to the market and build an effective trading strategy.
Advantages and disadvantages of financial leverage
Leverage can boost returns, but it also amplifies risks. Let’s explore the benefits and drawbacks:
Advantages of financial leverage
- Profit amplification: Profits from trades increase exponentially as the initial investment is multiplied by additional upfront capital. Leverage is best used in low-risk, short-term situations where high capital is needed.
- Flexibility: Instead of spending large sums of money to invest in risky projects, smart companies often use leverage to maximize business opportunities. This allows them to quickly seize attractive opportunities and exit when they feel too risky.
Disadvantages of financial leverage
- Loss amplification: Leverage is a double-edged sword. It can amplify profits, but it can also amplify losses, potentially exceeding your initial investment.
- Incurred fees: Compared to regular trading, your total transaction costs when trading with leverage will be higher, you have to pay many other types of fees such as insurance fees, margin fees, etc.
- Complexity: When using leverage, you need to closely monitor market developments and be ready to add capital whenever necessary. Otherwise, you may face the risk of losing capital.
History of leverage
Do you know that leveraged trading existed long before online trading platforms became popular?
In the early 20th century, when the US financial market was still in its infancy, investors quickly realized the power of leverage. With extremely high leverage ratios, they could control a much larger amount of assets than their initial capital. However, this led to serious financial crises, when the market fluctuate sharply and many investors were forced to liquidate their positions with heavy losses.
A typical example is the Great Depression in the 1930s. Excessive leverage in the stock market contributed to the crisis. When an investor received a margin call, it meant that their account was almost depleted and they were forced to add more money or liquidate their positions to avoid a total loss.
To use leverage safely and effectively, investors need to clearly understand how it works, accurately assess their risk tolerance and always comply with the regulations of the regulatory agency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, financial leverage is a powerful financial tool that allows businesses to magnify profits without requiring too much initial capital. However, like any other tool, leverage comes with certain risks. Carefully consider your financial situation, risk tolerance, and investment goals to maximize the benefits of leverage and minimize risks.
See more: