Interest rates are one of the most powerful macroeconomic forces influencing the foreign exchange market. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, a clear understanding of interest rate forex is crucial for grasping currency trends and making more informed decisions. What is interest rate forex, why do interest rates impact a currency’s value, and how can traders effectively use this information? This article will break down these concepts in a simple, practical way you can apply to your trading.
What is Interest Rate Forex?

Interest rate forex refers to the direct relationship between a country’s interest rates and the value of its currency in the foreign exchange market. In forex trading, the interest rate is a paramount factor that affects a currency’s value. When a country’s central bank adjusts its interest rate, it can cause the national currency to either strengthen or weaken significantly.
To put it simply, an interest rate is the cost of borrowing money or the return on a deposit. Every country has its own specific interest rate, set by its central bank, and this rate directly impacts the exchange rate through the flow of investment capital.
Therefore, in the forex market, the interest rate isn’t just an economic data point; it’s a “guiding compass” that helps traders forecast trends and identify more effective trading opportunities.
Why Does Interest Rate Affect the Forex Market?

In the forex market, interest rate forex is one of the most significant factors determining a currency pair’s value. The reason is simple: higher interest rates tend to attract capital inflows, as investors seek better returns. This increases demand for the local currency, which in turn causes its value to rise.
High Interest Rates Attract Investment Capital
When a country raises interest rates, international investors often move money into that currency to take advantage of the higher yield. For example, if the UK raises interest rates, the GBP may strengthen against the USD or EUR. This creates large fluctuations in currency pairs – opportunities for traders to enter trades.
Low Interest Rates Reduce a Currency’s Appeal
On the other hand, if a country lowers interest rates, holding that currency becomes less attractive. Investors may withdraw capital and move to economies with higher interest rates, weakening the domestic currency.
The Interest Rate Differential Between Countries
In forex trading, not only individual interest rates but also the interest rate differential between two currencies in a pair is an important factor. This is the basis for strategies such as the carry trade, where traders profit from borrowing a currency with a low interest rate and investing in a currency with a high interest rate.
See here:
- Catch up with Prop Firm Investment Trends for Better Trading
- Prop Firm Terminology: What Traders Must Know
- Prop Firm Expert Trading: New Path for Traders
- Tips To Identify A Reliable Prop Firm Market Leader
How to Calculate the Interest Rate in Forex
In the forex market, you don’t directly “calculate” the interest rate as an absolute number. Instead, you focus on the interest rate differential between the two currencies in a pair. This differential determines whether you will receive a payment or be charged a fee for holding a position overnight.
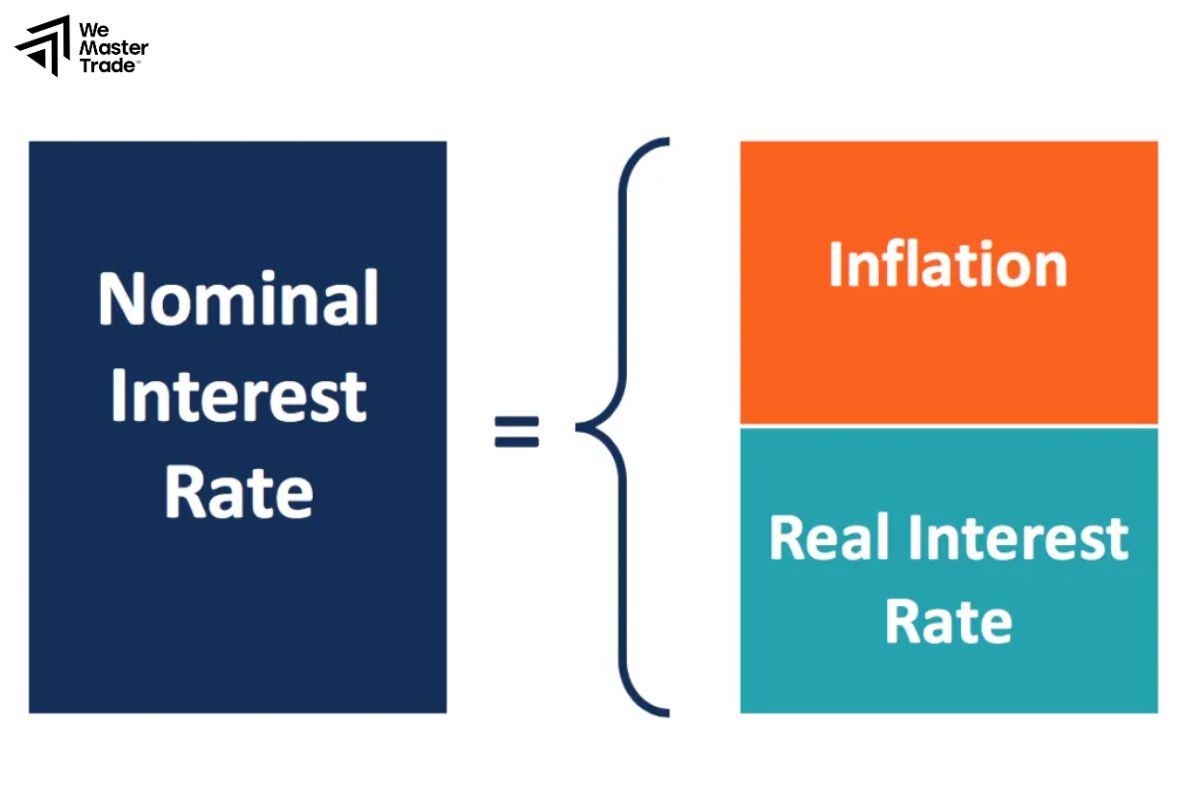
Basic Formula for Calculating Interest Rate Differential
Swap = (Buy Currency Interest Rate – Sell Currency Interest Rate) ÷ 365 × Trade Size × Exchange Rate
Example
Suppose you trade AUD/JPY, with:
- AUD Interest Rate: 4.35%
- JPY Interest Rate: 0.10%
Spread = 4.35% – 0.10% = +4.25%
When you buy AUD/JPY and hold the position overnight, you can earn a positive interest rate (positive swap). Conversely, if you sell AUD/JPY, you can pay a negative swap fee because you are holding a currency with a lower interest rate.
Risks When Trading Based on Interest Rates
While interest rate forex is a crucial component of fundamental analysis and can give traders a significant edge, misunderstanding the market’s reaction can expose you to unexpected risks. Here are some of the most common risks associated with trading based on interest rates:

High Volatility During Interest Rate News
Forex markets often react strongly to interest rate policy announcements from central banks. Even if interest rates remain unchanged, a “hawkish” or “doveish” statement in a press conference can cause prices to move hundreds of pips. Without a good risk management plan, you can easily get your stop-losses wiped out or fall into a state of panic.
Predicting the wrong direction of monetary policy
Trading on interest rate expectations can be attractive, but if you predict wrongly – for example, you expect the Fed to raise interest rates and they leave them unchanged or cut them – you will be “trapped” in the opposite direction. The market reacts not only to current numbers, but also to future expectations.
Risk of negative swaps
If you hold a position overnight and choose the wrong direction of the interest rate spread (e.g. sell a high-yielding currency and buy a low-yielding currency), you will be charged a negative swap every day. With large volumes and long periods of time, this fee can “eat away” profits or cause orders to lose money even if they have not been stopped-loss.
Leverage abuse
Even with a perceived advantage from interest rate forex, if you use too much leverage, even a small market movement can lead to heavy losses. Interest rates are a long-term factor, but high leverage amplifies short-term risks.
Conclusion
In short, interest rate forex is a core component of fundamental analysis that directly impacts currency strength and market trends. Understanding interest rates, how to calculate spreads and applying them to trading strategies such as carry trade or following interest rate news will help you improve efficiency and better control risks. Whether you are a new or experienced trader, monitoring interest rates and monetary policy will always be an important tool for active and sustainable forex trading.
See more: